Yes! You can use AI to fill out Form 1120-S, U.S. Income Tax Return for an S Corporation
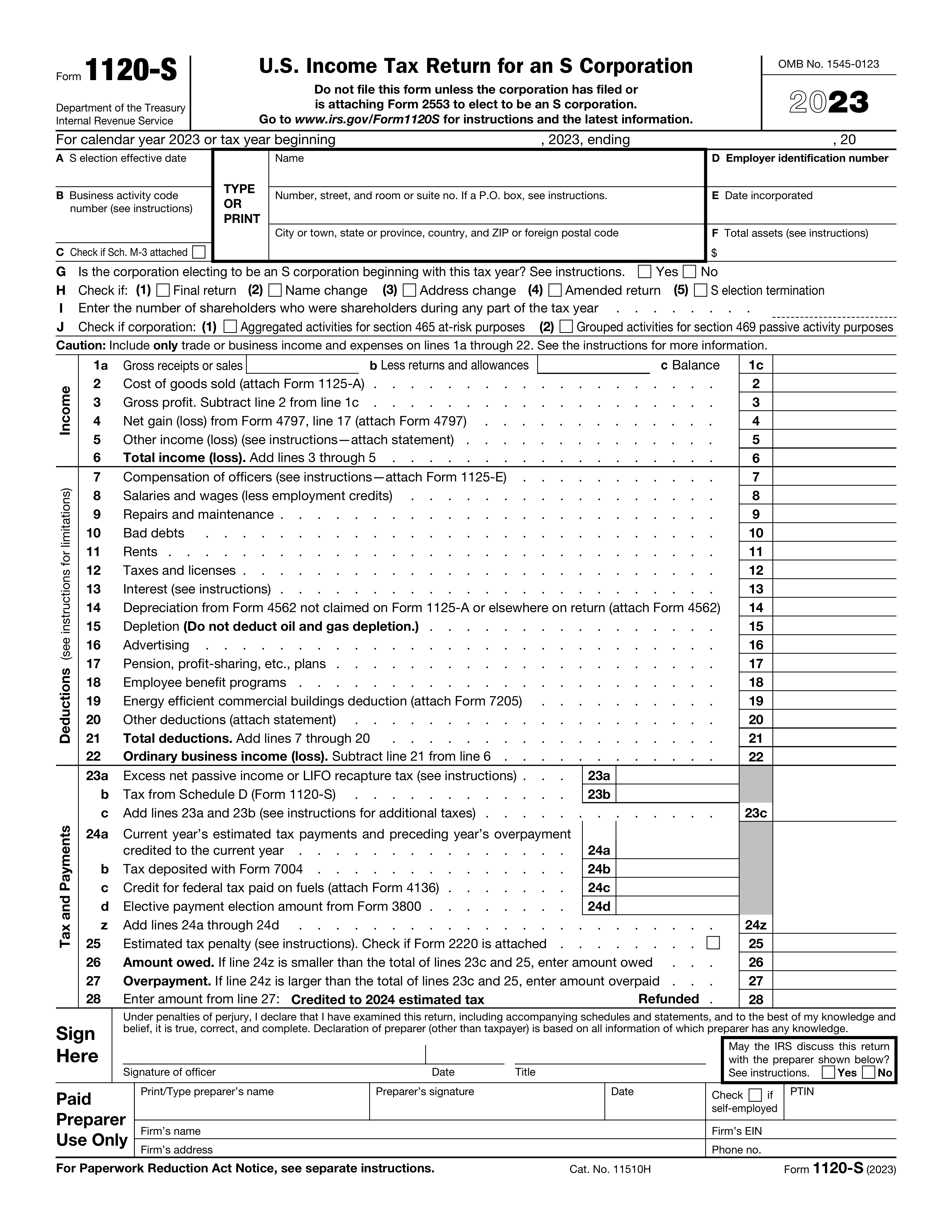
Form 1120-S, U.S. Income Tax Return for an S Corporation, is a tax document used by S corporations to report their income, losses, and deductions to the IRS. It's crucial for S corporations to file this form annually to ensure compliance with tax laws and to calculate their tax liability accurately.
Our AI automatically handles information lookup, data retrieval, formatting, and form filling.
It takes less than a minute to fill out Form 1120-S using our AI form filling.
Securely upload your data. Information is encrypted in transit and deleted immediately after the form is filled out.
Form specifications
| Form name: | Form 1120-S, U.S. Income Tax Return for an S Corporation |
| Form issued by: | Internal Revenue Service |
| Number of fields: | 378 |
| Number of pages: | 5 |
| Version: | 2023 |
| Form page: | https://www.irs.gov/forms-pubs/about-form-1120-s |
| Official download URL: | https://stinstafill.blob.core.windows.net/file-uploads/top-forms/1120s.pdf?sv=2023-08-03&st=2024-08-20T08%3A48%3A52Z&se=2054-08-20T08%3A48%3A52Z&sr=c&sp=r&sig=BwTakNzJbjCwWpnRziPrMIg5oVAalO1m7LPb27DVuK0%3D |
| Language: | English |
Instafill Demo: filling out a legal form in seconds
How to Fill Out Form 1120-S Online for Free in 2025
Are you looking to fill out a FORM 1120-S form online quickly and accurately? Instafill.ai offers the #1 AI-powered PDF filling software of 2025, allowing you to complete your FORM 1120-S form in just 37 seconds or less.
Follow these steps to fill out your FORM 1120-S form online using Instafill.ai:
- 1 Visit instafill.ai and select Form 1120-S.
- 2 Enter corporation's name and address.
- 3 Input business activity code and EIN.
- 4 Fill in income, deductions, and tax details.
- 5 Provide shareholder information and pro rata shares.
- 6 Sign and date the form electronically.
- 7 Check for accuracy and submit the form.
Our AI-powered system ensures each field is filled out correctly, reducing errors and saving you time.
Why Choose Instafill.ai for Your Fillable Form 1120-S Form?
Speed
Complete your Form 1120-S in as little as 37 seconds.
Up-to-Date
Always use the latest 2025 Form 1120-S form version.
Cost-effective
No need to hire expensive lawyers.
Accuracy
Our AI performs 10 compliance checks to ensure your form is error-free.
Security
Your personal information is protected with bank-level encryption.
Frequently Asked Questions About Form Form 1120-S
Form 1120-S is the U.S. Income Tax Return for an S Corporation. It is used by S corporations to report income, losses, and dividends to the IRS. S corporations are required to file this form annually to report their financial activities and to calculate any tax due. An S corporation is a special type of corporation created through an IRS tax election. An eligible domestic corporation can avoid double taxation (once to the corporation and again to the shareholders) by electing to be treated as an S corporation.
Your corporation is eligible to file Form 1120-S if it has elected to be treated as an S corporation by filing Form 2553, Election by a Small Business Corporation, with the IRS. To qualify for S corporation status, the corporation must meet certain requirements, including being a domestic corporation, having only allowable shareholders (which can include individuals, certain trusts, and estates but not partnerships, corporations, or non-resident alien shareholders), having no more than 100 shareholders, having only one class of stock, and not being an ineligible corporation (such as certain financial institutions, insurance companies, and domestic international sales corporations).
The deadline for filing Form 1120-S is March 15th for calendar year filers. If the corporation operates on a fiscal year basis, the form is due by the 15th day of the third month following the close of the fiscal year. If the due date falls on a weekend or a legal holiday, the deadline is extended to the next business day. Extensions of time to file can be requested by filing Form 7004, Application for Automatic Extension of Time To File Certain Business Income Tax, Information, and Other Returns, which can extend the filing deadline by six months.
Yes, Form 1120-S can be filed electronically. The IRS encourages electronic filing (e-filing) as it is more efficient and reduces the chance of errors. E-filing also allows for faster processing and acknowledgment of receipt by the IRS. Corporations can e-file Form 1120-S through an IRS-authorized e-file provider or through tax software that supports business tax returns.
To complete Form 1120-S, you will need detailed information about the corporation's income, deductions, credits, and other financial activities. This includes gross receipts or sales, cost of goods sold, dividends, interest, rents, royalties, capital gains and losses, and other income. You will also need information on deductions such as salaries and wages, repairs and maintenance, bad debts, taxes, and interest. Additionally, the form requires details on the corporation's balance sheet, including assets, liabilities, and shareholders' equity. Information on shareholders, including their share of income, losses, deductions, and credits, is also required.
Gross receipts or sales are reported on Line 1a of Form 1120-S. This includes all income received or accrued from the sale of goods or services, before any deductions. If your S corporation has more than one type of business activity, you may need to report each activity separately on Schedule K-1.
On Form 1120-S, you can claim deductions for ordinary and necessary business expenses. These include costs of goods sold, salaries and wages, rent, utilities, depreciation, and other expenses directly related to the operation of your S corporation. Specific deductions are detailed on various lines of the form, such as Line 2 for cost of goods sold, Line 7 for salaries and wages, and Line 20 for total deductions.
To calculate the total income or loss for your S corporation, start with the gross receipts or sales on Line 1a. Subtract the cost of goods sold (Line 2) to get the gross profit (Line 3). Then, subtract all allowable deductions (Lines 7 through 20) from the gross profit. The result is the ordinary business income (or loss), which is reported on Line 21. This figure is then carried over to Schedule K and allocated to shareholders on Schedule K-1.
Schedule K of Form 1120-S is used to report the S corporation's income, deductions, credits, and other items that are passed through to the shareholders. Each shareholder's share of these items is reported on Schedule K-1, which is attached to Schedule K. This allows shareholders to report their share of the S corporation's income or loss on their individual tax returns.
Shareholder information is reported on Schedule K-1 of Form 1120-S. For each shareholder, you must report their share of the S corporation's income, deductions, credits, and other items. This includes their percentage of ownership, which determines their share of the S corporation's income or loss. Each shareholder receives a copy of Schedule K-1 to include with their individual tax return.
The penalties for late filing of Form 1120-S can include a failure-to-file penalty, which is typically 5% of the unpaid taxes for each month or part of a month that the return is late, up to a maximum of 25% of the unpaid taxes. Additionally, there may be a failure-to-pay penalty, which is generally 0.5% of the unpaid taxes for each month or part of a month after the due date, up to 25% of the unpaid taxes. If both penalties apply in the same month, the combined penalty is 5% for each month or part of a month. Interest is also charged on taxes not paid by the due date, even if an extension to file is granted.
To amend a previously filed Form 1120-S, you must file Form 1120S-X, Amended U.S. Income Tax Return for an S Corporation. This form is used to correct errors or make changes to the original Form 1120-S. It's important to provide a detailed explanation of the changes being made and to attach any necessary supporting documentation. The amended return should be filed as soon as possible after the error is discovered to minimize any potential penalties and interest.
The S election effective date on Form 1120-S is crucial because it determines when the corporation's status as an S corporation begins. This date affects the corporation's tax obligations, including when it starts to pass through income, losses, deductions, and credits to its shareholders. The effective date is typically the first day of the corporation's tax year, but it can be a different date if the election is made after the start of the tax year, provided certain conditions are met. It's important to accurately report this date to ensure compliance with IRS regulations.
To report changes in corporate name or address on Form 1120-S, you should update the relevant sections of the form when you file your annual return. If the change occurs after you've already filed your return for the year, you should notify the IRS by writing to the address where you filed your last return. Include the corporation's EIN, the old and new name or address, and the date the change was effective. It's also advisable to inform the IRS of any changes in the responsible party's name or address.
The process for electing to be an S corporation involves filing Form 2553, Election by a Small Business Corporation, with the IRS. All shareholders must sign the form, indicating their consent to the election. The form must be filed by the 15th day of the third month of the tax year the election is to take effect, or at any time during the preceding tax year. It's important to ensure that the corporation meets all the eligibility requirements for S corporation status, including being a domestic corporation, having only allowable shareholders, and not having more than 100 shareholders. Once the election is made and approved by the IRS, the corporation will be treated as an S corporation for tax purposes.
Foreign income or transactions should be reported on Form 1120-S in accordance with U.S. tax laws. This includes reporting income from foreign sources and any transactions that may have tax implications, such as foreign tax credits or deductions. It's important to accurately report these amounts and to consult the instructions for Form 1120-S and any relevant international tax provisions to ensure compliance.
Digital assets, such as cryptocurrency, must be reported on Form 1120-S if they are part of the corporation's income, expenses, or assets. The IRS treats digital assets as property for tax purposes, so transactions involving digital assets should be reported in a manner similar to other property transactions. This includes reporting capital gains or losses from the sale or exchange of digital assets. Specific instructions for reporting digital assets can be found in the IRS guidance and the instructions for Form 1120-S.
The net unrealized built-in gain (NUBIG) is calculated by determining the difference between the fair market value and the adjusted basis of the corporation's assets at the time it became an S corporation. This calculation is necessary for corporations that were previously C corporations and have converted to S corporation status. The NUBIG must be reported on Form 1120-S if applicable, and specific instructions for this calculation can be found in the IRS guidelines and the instructions for Form 1120-S.
Schedule M-1 (Reconciliation of Income (Loss) per Books With Income (Loss) per Return) and Schedule M-2 (Analysis of Accumulated Adjustments Account, Other Adjustments Account, and Shareholders' Undistributed Taxable Income Previously Taxed) are used to reconcile the corporation's financial accounting income with its taxable income and to analyze changes in shareholders' equity accounts. Specific instructions for completing these schedules include detailing adjustments for items such as tax-exempt interest, nondeductible expenses, and differences in depreciation methods. The instructions for Form 1120-S provide detailed guidance on how to complete these schedules accurately.
Schedule M-3 (Net Income (Loss) Reconciliation for Corporations With Total Assets of $10 Million or More) is required for S corporations with total assets of $10 million or more. This schedule provides a more detailed reconciliation of book income to taxable income than Schedule M-1. If your corporation meets the asset threshold, you must file Schedule M-3 with Form 1120-S. The instructions for Form 1120-S and Schedule M-3 provide further details on the requirements and how to complete the schedule.
Compliance Form 1120-S
Validation Checks by Instafill.ai
1
Verifies that the corporation has filed or is attaching Form 2553 to elect to be an S corporation before filing Form 1120-S.
Ensures that the corporation has properly elected S corporation status by either filing Form 2553 or attaching it to Form 1120-S. This validation is crucial for confirming the corporation's eligibility to file as an S corporation. It checks the presence of Form 2553 to ensure compliance with IRS regulations. This step is essential for maintaining the corporation's S corporation status and avoiding potential penalties.
2
Confirms that the corporation's name, address, and Employer Identification Number (EIN) are accurately provided at the top of the form.
Confirms the accuracy of the corporation's identifying information, including its name, address, and EIN, at the top of Form 1120-S. This validation ensures that the IRS can correctly identify and process the tax return. It checks for any discrepancies or missing information that could lead to processing delays. Accurate identification information is vital for the integrity of the tax filing process.
3
Ensures that the tax year and the S election effective date are correctly indicated.
Verifies that the tax year and the effective date of the S corporation election are accurately reported on Form 1120-S. This validation ensures that the tax return corresponds to the correct tax period and that the S corporation election is applied from the appropriate date. It checks for any inconsistencies that could affect the corporation's tax obligations. Correctly indicating these dates is essential for compliance and accurate tax reporting.
4
Checks that the business activity code number is entered and verifies if Schedule M-3 is attached as required.
Ensures that the business activity code number is correctly entered on Form 1120-S, reflecting the corporation's primary business activity. This validation also checks for the attachment of Schedule M-3, if required, based on the corporation's total assets and receipts. It verifies compliance with IRS requirements for detailed financial reporting. Accurate reporting of the business activity code and attachment of Schedule M-3 are crucial for the IRS's understanding of the corporation's operations and financial status.
5
Validates that total assets are reported and confirms if the corporation is electing to be an S corporation beginning with this tax year.
Confirms that the total assets of the corporation are accurately reported on Form 1120-S. This validation also checks whether the corporation is making an election to be treated as an S corporation starting with the current tax year. It ensures that the financial information provided is complete and accurate, which is essential for tax assessment. Additionally, it verifies the corporation's intent to change its tax status, if applicable, ensuring compliance with IRS regulations.
6
Ensures that applicable boxes for final return, name change, address change, amended return, or S election termination are checked.
The AI software ensures that the appropriate boxes indicating a final return, name change, address change, amended return, or S election termination are accurately checked. This validation is crucial for the IRS to understand the nature of the filing and any significant changes affecting the S Corporation. It checks for consistency and completeness in the form's declarations, ensuring that all relevant changes are properly documented. This step is vital for maintaining the integrity and accuracy of the tax return process.
7
Verifies that the number of shareholders during the tax year is entered and checks if the corporation has aggregated or grouped activities for specific tax purposes.
The AI software verifies that the number of shareholders during the tax year is correctly entered, reflecting the corporation's ownership structure accurately. It also checks whether the corporation has aggregated or grouped activities for specific tax purposes, which is essential for determining the correct tax treatment. This validation ensures that the form accurately represents the corporation's shareholder information and any grouped activities, which are critical for tax compliance and reporting. It aids in preventing discrepancies that could lead to audits or penalties.
8
Confirms that income and deductions are accurately reported, with all required forms and statements attached for specific line items.
The AI software confirms that all income and deductions are accurately reported on the form, ensuring that the financial information aligns with the corporation's records. It checks for the presence of all required forms and statements that must accompany specific line items, ensuring comprehensive and accurate reporting. This validation is crucial for the IRS to assess the corporation's tax liability correctly. It helps in minimizing errors that could affect the corporation's tax obligations and potential refunds.
9
Validates the calculation and reporting of tax and payments, including any estimated tax penalty.
The AI software validates the calculation and reporting of tax and payments, ensuring that all figures are accurate and in compliance with IRS regulations. It specifically checks for the correct reporting of any estimated tax penalties, which are crucial for the corporation's tax compliance. This validation ensures that the corporation's tax liabilities and payments are accurately reflected, preventing potential issues with the IRS. It is a critical step in ensuring the corporation meets its tax obligations accurately and timely.
10
Ensures that the form is signed and dated, and preparer information is provided if applicable.
The AI software ensures that the form is properly signed and dated, confirming the authenticity and timeliness of the submission. It also verifies that preparer information is provided if applicable, ensuring that all parties involved in the preparation of the tax return are accounted for. This validation is essential for the IRS to verify the legitimacy of the tax return and the individuals responsible for its preparation. It helps in maintaining the integrity of the tax filing process and ensures compliance with IRS requirements.
11
Checks that Schedule B is completed for other information, including accounting method, business activity, and shareholder information.
Ensures that Schedule B is accurately completed, capturing essential details such as the corporation's accounting method, primary business activity, and comprehensive shareholder information. This validation confirms that all required fields in Schedule B are filled out, providing a clear overview of the corporation's operational and financial framework. It verifies that the information aligns with the corporation's records and the IRS requirements for an S Corporation. This step is crucial for maintaining compliance and ensuring that the tax return reflects the corporation's actual business practices and shareholder structure.
12
Verifies that Schedule K is filled out for shareholders' pro rata share items, detailing income, deductions, credits, and other relevant information.
Confirms that Schedule K is meticulously prepared, detailing each shareholder's pro rata share of income, deductions, credits, and other pertinent items. This validation ensures that the distribution of financial items among shareholders is accurately represented, reflecting the corporation's financial activities and tax obligations. It checks for completeness and accuracy in reporting, ensuring that shareholders receive correct information for their individual tax filings. This step is vital for the integrity of the tax return and for the shareholders' compliance with their tax responsibilities.
13
Confirms that Schedule L is prepared for balance sheets per books and Schedule M-1 for reconciliation of income per books with income per return.
Ensures that Schedule L is accurately prepared, presenting the corporation's balance sheets as per its books, and that Schedule M-1 correctly reconciles the income reported in the books with the income reported on the tax return. This validation checks for discrepancies between the corporation's financial records and its tax filings, ensuring consistency and accuracy. It verifies that all financial statements are in alignment, providing a transparent view of the corporation's financial health. This step is essential for detecting and correcting any inconsistencies that could affect the corporation's tax liabilities.
14
Ensures that, if applicable, Schedule M-2 is completed for analysis of accumulated adjustments account and other adjustments.
Verifies that Schedule M-2 is completed when applicable, providing a detailed analysis of the accumulated adjustments account and any other adjustments. This validation ensures that all adjustments affecting the corporation's equity are accurately reported and justified. It checks for the completeness of the schedule, ensuring that it reflects all necessary adjustments in accordance with IRS guidelines. This step is crucial for maintaining the accuracy of the corporation's financial statements and for ensuring compliance with tax regulations.
15
Validates that all attachments and additional forms are included as required by the instructions for each section.
Confirms that all necessary attachments and additional forms are included with the tax return, as specified by the IRS instructions for each section. This validation ensures that the tax return is complete and that all required documentation is provided to support the information reported. It checks for the presence of each required attachment, ensuring that the corporation meets all filing requirements. This step is essential for avoiding delays or issues with the processing of the tax return and for ensuring full compliance with IRS regulations.
Common Mistakes in Completing Form 1120-S
A critical mistake is not filing or attaching Form 2553, Election by a Small Business Corporation, before submitting Form 1120-S. This form is essential for a corporation to elect S corporation status. Without it, the IRS will not recognize the corporation as an S corporation, leading to potential tax liabilities as a C corporation. To avoid this, ensure Form 2553 is completed accurately and submitted timely, ideally within two months and 15 days after the start of the tax year the election is to take effect.
Submitting Form 1120-S with an incorrect or missing Employer Identification Number (EIN) is a common error that can delay processing. The EIN is crucial for the IRS to identify the corporation and process its tax return. To prevent this mistake, double-check the EIN on all documents before submission. If the corporation does not have an EIN, it must apply for one through the IRS before filing Form 1120-S.
Incorrectly stating or omitting the S election effective date on Form 1120-S can lead to misunderstandings about when the S corporation status begins. This date is vital for determining the tax year in which the S corporation election takes effect. To ensure accuracy, verify the effective date with the date on Form 2553 and consistently use this date on all related tax documents.
Reporting an incorrect business activity code number on Form 1120-S can misrepresent the corporation's primary business activities to the IRS. This code helps the IRS classify the corporation for statistical purposes and ensure compliance with tax laws. To avoid this error, carefully review the North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) codes and select the one that best matches the corporation's primary business activity.
Failing to attach Schedule M-3 when required is a mistake that can lead to penalties. Schedule M-3 is necessary for corporations with total assets of $10 million or more to reconcile financial accounting net income with taxable income. To prevent this oversight, assess the corporation's total assets and ensure Schedule M-3 is completed and attached if the threshold is met or exceeded.
Accurate reporting of total assets is crucial for the correct assessment of an S Corporation's financial health and tax obligations. Mistakes in this area can lead to discrepancies in the tax return, potentially triggering audits or penalties. To avoid this, ensure that all assets are accurately valued and reported according to the latest IRS guidelines. Regular audits and reviews of asset records can help maintain accuracy and compliance.
Failing to check the appropriate boxes for a final return or amendments can result in the IRS not recognizing the return's status, leading to processing delays or incorrect tax assessments. It is essential to carefully review the form instructions to determine if the return is final or amended and to mark the correct boxes accordingly. This attention to detail ensures that the IRS processes the return as intended, avoiding unnecessary complications.
Reporting an incorrect number of shareholders can affect the S Corporation's eligibility for certain tax treatments and credits. This mistake often stems from not keeping shareholder records up to date or misunderstanding the requirements for shareholder counting. To prevent this, maintain accurate and current records of all shareholders and consult the IRS guidelines or a tax professional to ensure the correct number is reported.
Accurate reporting of income and deductions is fundamental to complying with tax laws and avoiding penalties. Errors in this area can result from oversight, misunderstanding of tax rules, or incorrect data entry. To minimize mistakes, use reliable accounting software, double-check entries against financial records, and seek advice from tax professionals when uncertain about the classification or calculation of income and deductions.
Omitting required forms and statements can lead to incomplete tax returns, which may delay processing or result in the disallowance of certain deductions or credits. It is important to review the form instructions thoroughly to identify all required attachments for specific line items. Organizing and reviewing all documentation before filing can help ensure that no necessary forms or statements are overlooked.
A frequent error in filing Form 1120-S is the incorrect calculation of tax and payments. This can lead to discrepancies in the amount owed or refunded, potentially resulting in penalties or interest charges. To avoid this, it is crucial to double-check all calculations, including taxable income, deductions, and credits. Utilizing tax software or consulting with a tax professional can help ensure accuracy. Additionally, reviewing the IRS guidelines for S Corporations can provide clarity on how to correctly compute taxes and payments.
Failing to sign or date Form 1120-S is a common oversight that can invalidate the tax return. The IRS requires a signature from an authorized officer of the corporation to process the return. To prevent this mistake, ensure that the form is signed and dated before submission. It's also advisable to keep a copy of the signed return for your records. Establishing a checklist that includes verifying the signature and date can serve as a helpful reminder.
When a tax preparer is used to complete Form 1120-S, omitting their information is a mistake that can delay processing. The IRS requires the preparer's name, signature, PTIN, and other relevant details if someone other than the taxpayer prepares the return. To avoid this error, ensure that all preparer information is accurately filled out and included with the submission. Communication with the preparer about their responsibilities and the information required can help streamline this process.
An incomplete Schedule B can lead to questions or audits from the IRS, as it provides essential information about the corporation's activities and affiliations. To prevent this, thoroughly review Schedule B and ensure all applicable questions are answered accurately. Gathering all necessary information before beginning the form can help ensure completeness. Consulting the instructions for Schedule B can also clarify what information is required.
Inaccuracies in Schedule K can affect the shareholders' tax liabilities, as it details their pro rata share items. Errors here can lead to incorrect tax filings for shareholders and potential penalties. To avoid this, meticulously review all entries on Schedule K for accuracy. It's beneficial to cross-verify the information with the corporation's financial records. Engaging a tax professional to review Schedule K can also help ensure that all information is correctly reported.
Failing to fully complete Schedule L, which details the corporation's balance sheets per books, is a frequent oversight. This schedule is crucial for providing a clear financial picture of the corporation at the beginning and end of the tax year. To avoid this mistake, ensure all assets, liabilities, and equity accounts are accurately reported. Double-check the figures against the corporation's financial records to ensure consistency and completeness.
Incorrectly reconciling the corporation's book income with its taxable income on Schedule M-1 is a common error. This reconciliation is essential for identifying differences between financial accounting and tax reporting. To prevent this mistake, carefully review the corporation's financial statements and tax return to accurately identify and report any discrepancies. Consulting with a tax professional can also help ensure the reconciliation is done correctly.
Neglecting to complete Schedule M-2, which tracks the corporation's accumulated adjustments account (AAA) and other equity accounts, when applicable, can lead to inaccuracies in the tax return. This schedule is vital for S corporations to report changes in shareholder equity. To avoid this oversight, determine if Schedule M-2 is required based on the corporation's financial activities and ensure all relevant changes in equity are accurately reported.
Omitting necessary attachments and additional forms required by the IRS is a mistake that can delay the processing of the tax return. These attachments may include statements, schedules, or other documentation that supports the information reported on Form 1120-S. To prevent this error, thoroughly review the IRS instructions for Form 1120-S to identify all required attachments and ensure they are included with the tax return. Keeping a checklist of required documents can also help ensure nothing is overlooked.
Saved over 80 hours a year
“I was never sure if my IRS forms like W-9 were filled correctly. Now, I can complete the forms accurately without any external help.”
Kevin Martin Green
Your data stays secure with advanced protection from Instafill and our subprocessors



Robust compliance program
Transparent business model
You’re not the product. You always know where your data is and what it is processed for.
ISO 27001, HIPAA, and GDPR
Our subprocesses adhere to multiple compliance standards, including but not limited to ISO 27001, HIPAA, and GDPR.
Security & privacy by design
We consider security and privacy from the initial design phase of any new service or functionality. It’s not an afterthought, it’s built-in, including support for two-factor authentication (2FA) to further protect your account.
Fill out Form 1120-S with Instafill.ai
Worried about filling PDFs wrong? Instafill securely fills 1120s forms, ensuring each field is accurate.